Cute Animals
Breakthrough Targets Make Prostate Cancer Treatments Stronger
Quick Smiles:
- Scientists found new weaknesses in prostate cancer cells that can boost treatments.
- Blocking enzymes PDIA1 and PDIA5 makes cancer cells more vulnerable to medication.
- Early studies show promise for improving outcomes in advanced prostate cancer.
Researchers have uncovered a new way to make prostate cancer treatments more powerful by revealing a weakness in the cancer cells. They discovered that two enzymes, PDIA1 and PDIA5, help prostate cancer cells survive, grow, and resist therapy.
These enzymes act as “molecular bodyguards” for the androgen receptor, protecting this key protein that drives cancer growth.
When PDIA1 and PDIA5 are blocked, the androgen receptor becomes unstable, leading to cancer cell death and tumor shrinkage in laboratory and animal studies.
Combining drugs that block these enzymes with enzalutamide, a common prostate cancer medication, showed a notable increase in effectiveness.
“This is an exciting step forward,” said Professor Jianling Xie, lead author of the study.
Resistance to therapy is a big hurdle for prostate cancer patients, but this discovery may help expand treatment options and improve survival for men with advanced stages.
Professor Luke Selth of Flinders University explained, “We’ve discovered a previously unknown mechanism that prostate cancer cells use to protect the androgen receptor, which is a key driver of the disease.”
“By targeting these enzymes, we can destabilize the AR and make tumors more vulnerable to existing therapies like enzalutamide.”
Dr. Xie noted that the new combination worked well in patient tumor samples and in mice, giving hope for future clinical trials.
“Our findings show that PDIA1 and PDIA5 are not just helpers of cancer growth but they’re also promising targets for new treatments that could work alongside existing drugs.”
This research also revealed that blocking the enzymes damaged the cells’ mitochondria, causing stress and further weakening the cancer cells. “It’s like cutting off both the fuel and the engine at the same time,” shared Xie.
Professor Selth emphasized that more research is needed to guarantee the safety and effectiveness of these new treatment strategies.
New discoveries like this shine a light on the path to better therapies, offering hope for patients and families affected by prostate cancer.

-
 Cute Animals2 years ago
Cute Animals2 years agoPuppy Love Patrol: Service Dog Swoons Over K9 Officer Neighbor
-
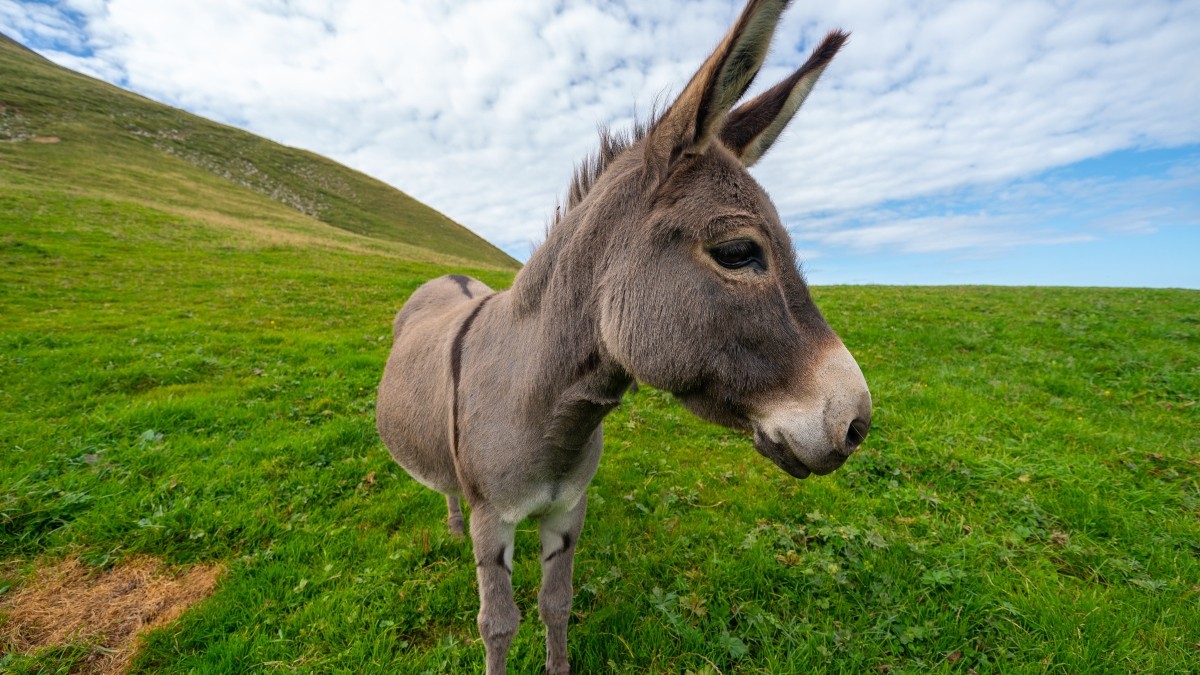

 Cute Animals2 years ago
Cute Animals2 years agoHugs, Hooves, and Happiness: Newborn Donkey Steals Hearts by Demanding Affection [Video]
-

 Cute Animals2 years ago
Cute Animals2 years agoWATCH: A German Shepherd’s Surprising Parenting Instinct for Lost Ducklings!
-

 Cute Animals2 years ago
Cute Animals2 years agoPetty Pup Pulls Off Hilarious Bone Heist [Video]
-

 Heroes2 years ago
Heroes2 years agoA Lost Dog’s Bark Leads to a Lifesaving Discovery
-

 Cute Animals2 years ago
Cute Animals2 years ago“Pure Love”: Adopted Rescue Dog Can’t Hide How Grateful He Is [Video]
-

 Cute Animals2 years ago
Cute Animals2 years agoTiny but Mighty: Cat with Dwarfism Becomes Internet Star as Owners Adapt Backyard for Her Comfort
-

 Cute Animals2 years ago
Cute Animals2 years agoAdorable Puppy Steals Hearts After a Tiring Swim [Video]